Quality Assurance: Difference between revisions
Ttenbergen (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
Ttenbergen (talk | contribs) m (→Data Flow at the Critical Care and Medicine Database: replace data flow image with imagemap as it used to be on front page.) |
||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
== Data Flow at the Critical Care and Medicine Database == | == Data Flow at the Critical Care and Medicine Database == | ||
<imagemap> | |||
Image:CCMDB Description.png|700px|alt=Description of CCMDB sources and outputs | |||
rect 8 79 143 101 [[Data available in the Critical Care and Medicine Database]] | |||
rect 9 104 141 128 [[Demographics]] | |||
rect 9 132 141 155 [[ADT]] | |||
rect 9 158 141 182 [[APACHE_II]] | |||
rect 9 188 141 211 [[Diagnostic Data available in the Critical Care and Medicine Database]] | |||
rect 9 215 141 237 [[Procedure Data available in the Critical Care and Medicine Database]] | |||
rect 9 244 141 266 [[Acquired_Diagnosis_/_Complication]] | |||
rect 8 269 142 293 [[Pharmacy_collection]] | |||
rect 75 297 139 379 [[TISS]] | |||
rect 8 384 143 407 [[Projects]] | |||
rect 15 404 138 427 [[QA_Infection_CLI]] | |||
rect 14 428 137 452 [[QA_Infection_VAP]] | |||
rect 14 454 140 477 [[Database Request Process]] | |||
rect 7 509 140 532 [[Category:External Source]] | |||
rect 49 533 141 556 [[DSM_Lab_Extract]] | |||
rect 5 563 140 604 [[Validation_against_Patient_Registry_Data]] | |||
rect 168 209 228 366 [[Data_Collector]] | |||
rect 319 245 377 322 [[Data_Processor]] | |||
rect 282 330 379 356 [[Data_Processing]] | |||
rect 438 245 496 322 [[Statistician]] | |||
rect 437 330 497 356 [[Statistical_Analysis]] | |||
rect 481 68 649 91 [[Postal_Code_field#Data_Use]] | |||
rect 666 84 801 106 [[Avoidable Days in ICU]] | |||
rect 528 96 582 120 [[Age]] | |||
rect 589 111 776 134 [[Night Time Discharges]] | |||
rect 538 137 664 161 [[LOS]] | |||
rect 670 137 766 160 [[Bed_occupancy]] | |||
rect 533 167 641 190 [[Patient flow]] | |||
rect 643 168 809 190 [[Readmission]] | |||
rect 577 197 676 218 [[ARO]] | |||
rect 679 197 811 218 [[Ulcers_-_Decubitus_only]] | |||
rect 572 223 626 245 [[Acuity]] | |||
rect 629 222 777 245 [[Central Line Tracking]] | |||
rect 596 250 715 272 [[Confusion_Assessment_Method]] | |||
rect 720 248 812 273 [[Ventilator Utilization Ratio]] | |||
rect 558 278 704 300 [[Nursing Workload]] | |||
rect 708 276 814 300 [[CRRT]] | |||
rect 626 302 715 325 [[QA_Infection_CLI]] | |||
rect 717 320 814 343 [[QA_Infection_VAP]] | |||
rect 610 344 734 367 [[CRRT]] | |||
rect 679 374 790 437 [[Reporting]] | |||
rect 625 448 692 511 [[Chart Review Lists]] | |||
rect 709 446 794 509 [[Statistical_Analysis]] | |||
rect 595 524 676 564 [[Resource Use]] | |||
rect 576 573 690 654 [[Before/After comparisons for QI Interventions]] | |||
rect 698 523 789 607 [[Base Population for Research]] | |||
rect 468 547 562 641 [[Database_Request_Process]] | |||
rect 347 569 439 649 [[Critical_Care_Vital_Sign_Monitor]] | |||
rect 233 535 318 615 [[Manitoba_Centre_for_Health_Policy]] | |||
rect 238 624 337 646 [[Publications]] | |||
</imagemap> | |||
== Factors Affecting Quality of Data == | == Factors Affecting Quality of Data == | ||
Revision as of 09:14, 2023 March 16
This article presents the content of Julie's Quality Assurance presentation from the data collection meeting on April 8 2009.
For discussion or questions re. the concepts of QA or Julie's presentation please post your discussions in this article as usual.
What is QA?
An integrated system of activities involving:
- planning
- quality control
- quality assessment
- reporting and
- quality improvement
to ensure that a product or service meets standards of quality with stated levels of confidence.
History of QA
- Started early 19th century in Great Britain during the Industrial Revolution emphasis on product inspection
- Early 20th century by manufacturers and included quality processes
- WWII, US used quality processes in manufacturing of bullets and rifles- sampling technique of inspection
- Japan’s Quality Revolution on automobiles and electronics – focus on improving the organization processes thru people
- 20th century, US introduced Total Quality Management (TQM) – quality on the entire organization
- 21st century, moved beyond manufacturing into service, healthcare, education and government sector
QA in Healthcare
- “All the arrangements and activities that are meant to safeguard, maintain, and promote the quality of care”
- “Set of activities that are carried out to set standards and to monitor and improve performance so that the care provided is as effective and safe as possible”
What is QA to a Medical Database?
- Our product is medical data
- General Goal: To assure the users of these data that they meet standards of quality with stated levels of confidence
- Specific Goal: To determine quantitatively the level of confidence of our data, and to improve that level of quality if needed.
- “Standards” is something set up as a rule for measuring or a model to be followed.
- Quality does not mean “BEST” but may mean “BEST for certain conditions”
- Medically sound, Defensible, Of know quality
- Level of confidence
- Degree of certainty
- Degree of assurance
Principles of QA
- Oriented toward meeting the needs and expectations of the clients
- Focuses on systems and processes
- Uses quantitative data to analyze the problem in the processes
- Encourages a team approach to problem solving and quality improvement
Data Flow at the Critical Care and Medicine Database
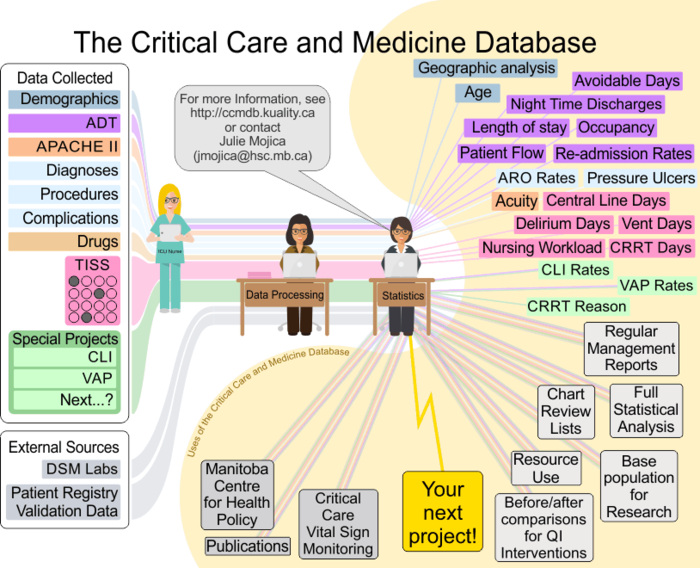
Factors Affecting Quality of Data
- Data collection phase
- Sources of data (what, where and how each element is collected)
- Timing of recording
- Hospital protocols/system
- Guidelines (clarity / comprehensive)
- Volume of patients
- Hardwares (PDAs, PCs)
- Memory and capabilities, etc.
- Softwares (Handibase, ACCESS, TMSX & MEDTMS, SAS)
- User friendly/confusing
- Easy/hard to use
- Capabilities in handling large data volume
- Error control features
- Etc.
- Human Factor
- Staff training for new staff
- Staff compliance on the on-going changes in the process
- Staff motivation
- Staff perception on workload
- etc.
Key Elements of QA
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
- Hardware & Software
- Training
- Statistical considerations
- Monitoring data quality indicators
- Audits
- Documentation
Data Quality Indicators
In assuring the quality of data, the usual concern is to minimize ( or if possible eliminate) errors in the measurement process
Two indicators related in evaluating errors Accuracy and Precision.
Accuracy
Refers to the closeness of the measurement to its true or expected or accepted value.
Precision
Refers to the closeness of the repeated measurements made under the same conditions.
Advantages of QA
- Produces well-documented, reliable and defensible data
- Enhances confidence and credibility of the organization
- Results in efficient use of resources – personnel, equipment and finances
- Improves the staff’s morale and commitment
Conclusion
- QA is not an easy task
- Requires collaboration, cooperation and commitment of staff and management
- Challenge to improve quality of our product